Unwin’s formula gives the diameter of the rivet hole for a given plate: d = 6*t0.5
where t = Thickness of plate in mm and
d = Diameter of the rivet in mm, which is used to denote the dimension of the rivet.
Types of Rivets:
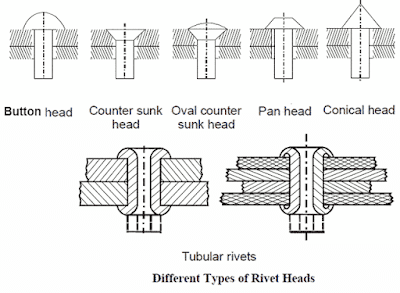
For steel plates, the rivets are made of low-carbon steel. Copper rivets add resistance against corrosion, and aluminum rivets can lower the structure's weight.Rivets with countersunk heads and oval countersunk rivets shown in the bottom image are not as strong as button-head rivets. The countersunk head and oval countersunk rivets are used only when protruding rivet heads are objectionable. Pan heads and conical heads are less frequently used and are difficult to produce. Tubular rivets have a special deviation from the solid rivet shank. Tubular rivets are used in aircraft.
Types of Riveted Joints:
The classification of riveted joints can be done in the following ways:1. According to the purpose of rivets:
Based on purpose, the riveted joints can be classified into three types:1.1 Strong Joints: Strong rivet joints are the only criterion for strength. These joints are used in engineering structures such as trusses, beams, and machine frames.
1.2 Tight Joints: Tight rivet joints provide strength and are leakproof against low pressures. Joints in reservoirs, containers, and tanks fall into this group.
1.3 Strong Tight Joints: Strong, tight rivet joints are used in boilers and pressure vessels and ensure strength and leakproofness.
Classification of rivets based on purpose has no sound basis and is arbitrary. This classification of rivets helps to understand the basis of design and manufacturing.
2. According to the position of the plates connected:
According to the position of plates, connected riveted joints are classified into two types:2.1 Lap joint: In a lap joint, the edges of plates are simply laid over each other and riveted.
2.2 Butt joint: In Butt, joint plates lie in the same plane and are joined through cover plates.


Post a Comment
Post a Comment